Brand Research: Apple’s Retail Store Market Strategy
This week Apple announced their new $3,500 mixed reality headset. We took the opportunity to look at their retail store footprint and what it says about their market strategy.
Apple is an upscale mass-market brand. Its iPhones are ubiquitous and Mac products widely adopted.
Their physical store presence is as much branding & product showcase as pure play retail (in other words - the store’s goals aren’t only to sell in-store). The stores also drive value as repair shops and online order pickups.
Given these store goals, a strong market planning strategy would emphasize:
Wide reach
“Destination” locations
High foot-traffic areas
Convenient to customers
What does the data say against these goals?
In this post we’re looking at the analytics behind Apple’s US location footprint, surrounding area characteristics, and retail store market strategy.
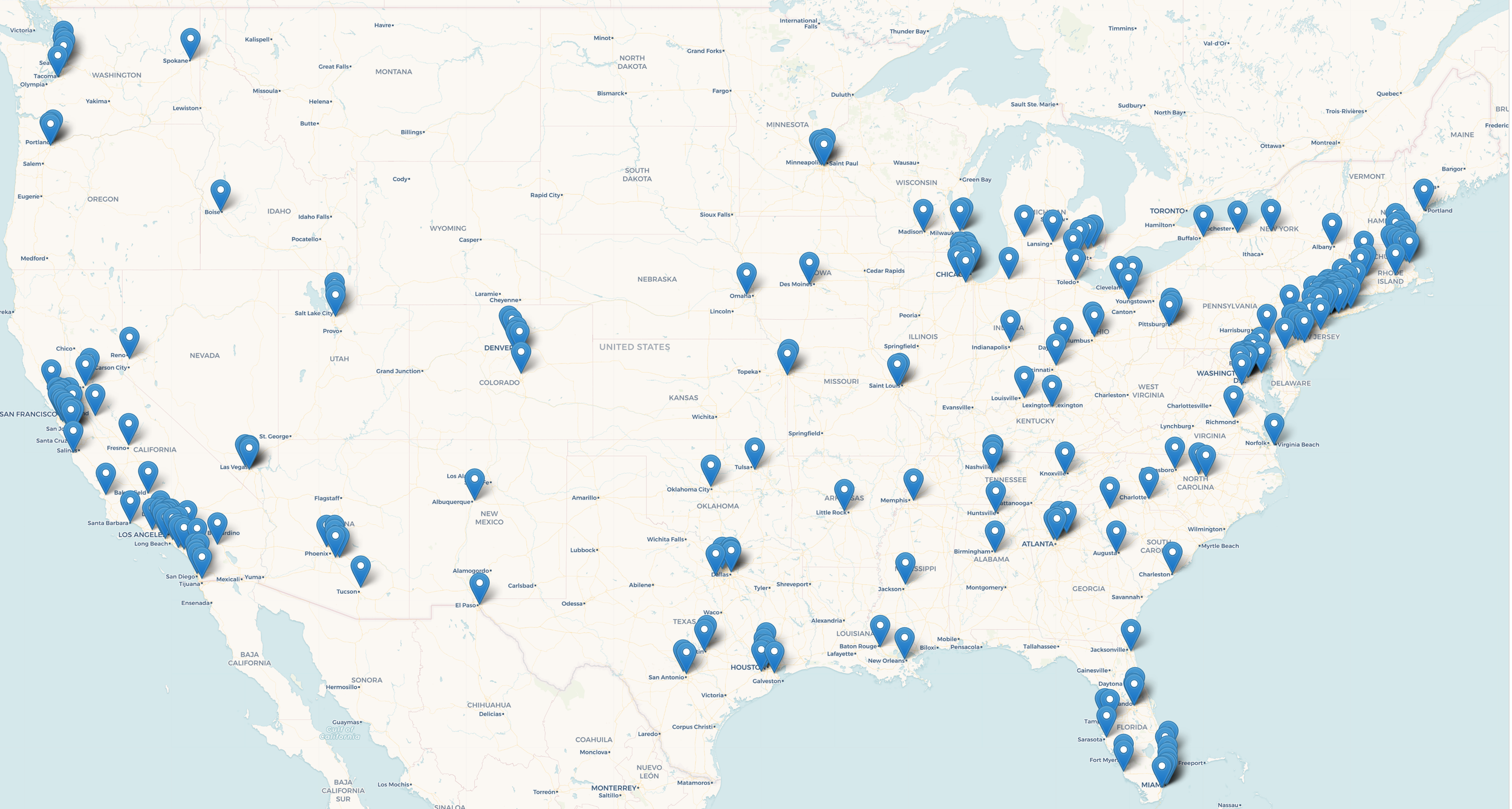
Apple’s Location Footprint
Apple operates 272 stores in the United States. These locations are spread across 45 states and 105 metro areas, loosely following population size.
The stores are spread across dense urban areas and high-income suburban areas. We pulled the data within 5-miles of every store and found that the typical location has:
240,000 residential population
~57% of working-age adults with full-time employment
150,000+ jobs
$45,000 household income
Big picture, this segmentation makes sense. Apple doesn’t need to flood the market with locations like, for example, Chipotle (read more on them here). They have their flagship locations and then spread into the wealthier suburbs around cities.
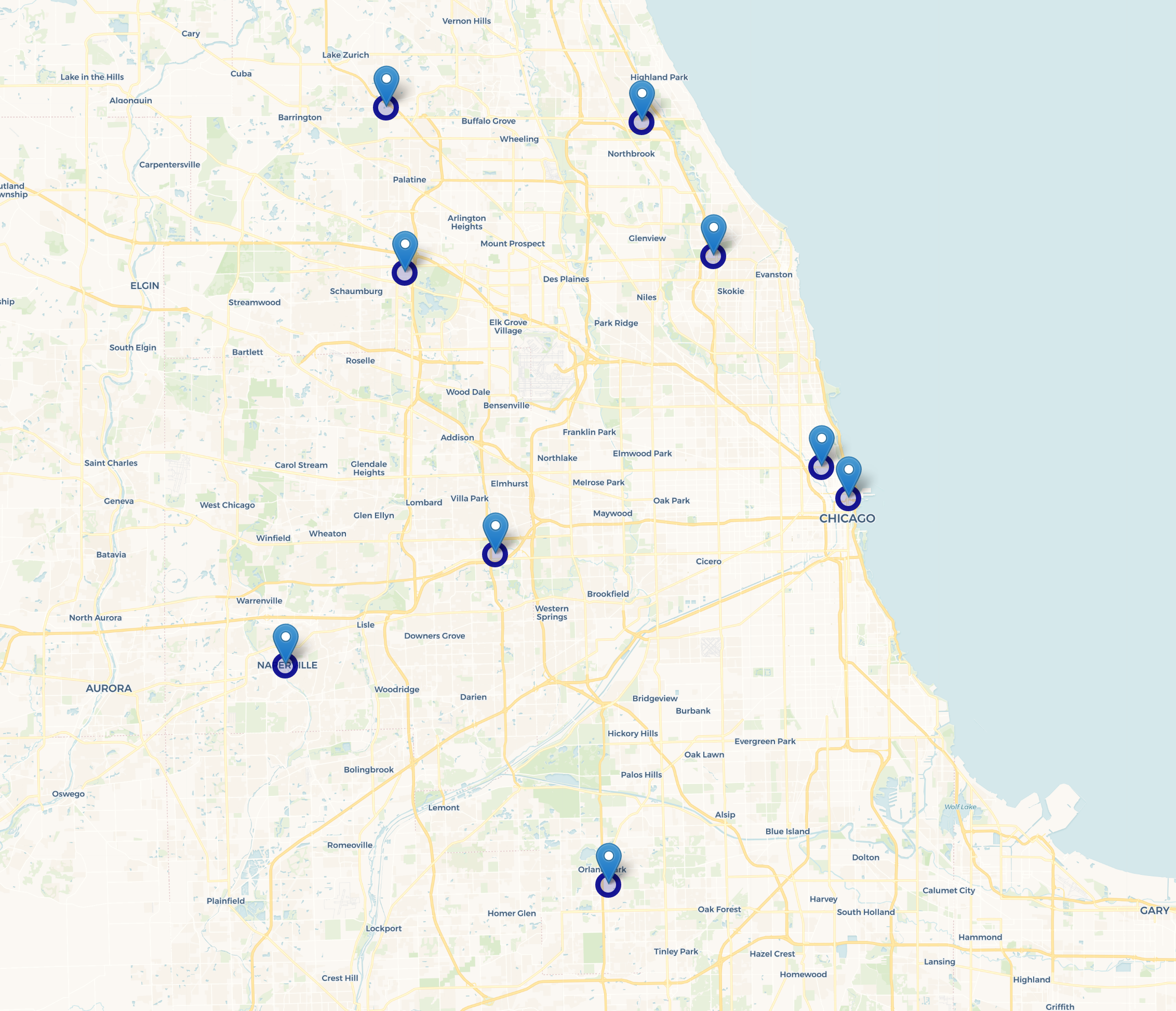
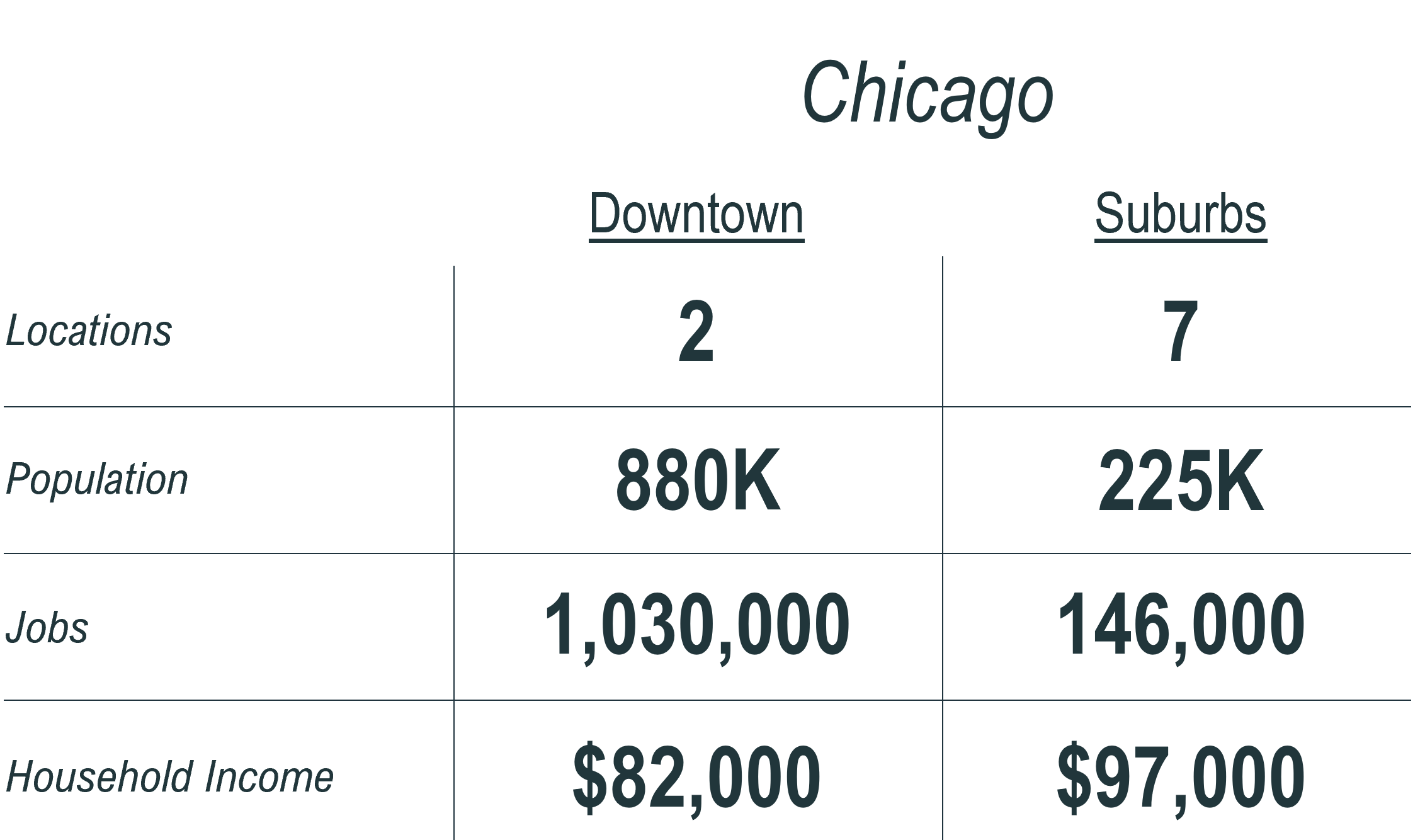
Consider the Chicago metro area - the third most populated CBSA in the country. Apple has 9 stores but just two are in the core downtown.
The two downtown locations have surrounding area population (5-miles) of 750,000-1,000,000. Both have over 1,000,000 jobs located in the catchment area.
Conversely, the suburban locations have lower surrounding area population (150,000-425,000) and jobs but ~20% higher income.
The market planning is geared toward reach and finding the target population over market density.
Collectively, we estimate that Apple reaches ~25% of the US population within just a 5-mile radius of its 272 stores - a remarkably efficient footprint.
Consider that Walmart is estimated to reach 85% of the population within a 10-mile radius of its 4,717 stores. This equates to ~60,000 unique individuals per store compared to Apple’s 300,000 (in half the radius size).
The Area Around Apple
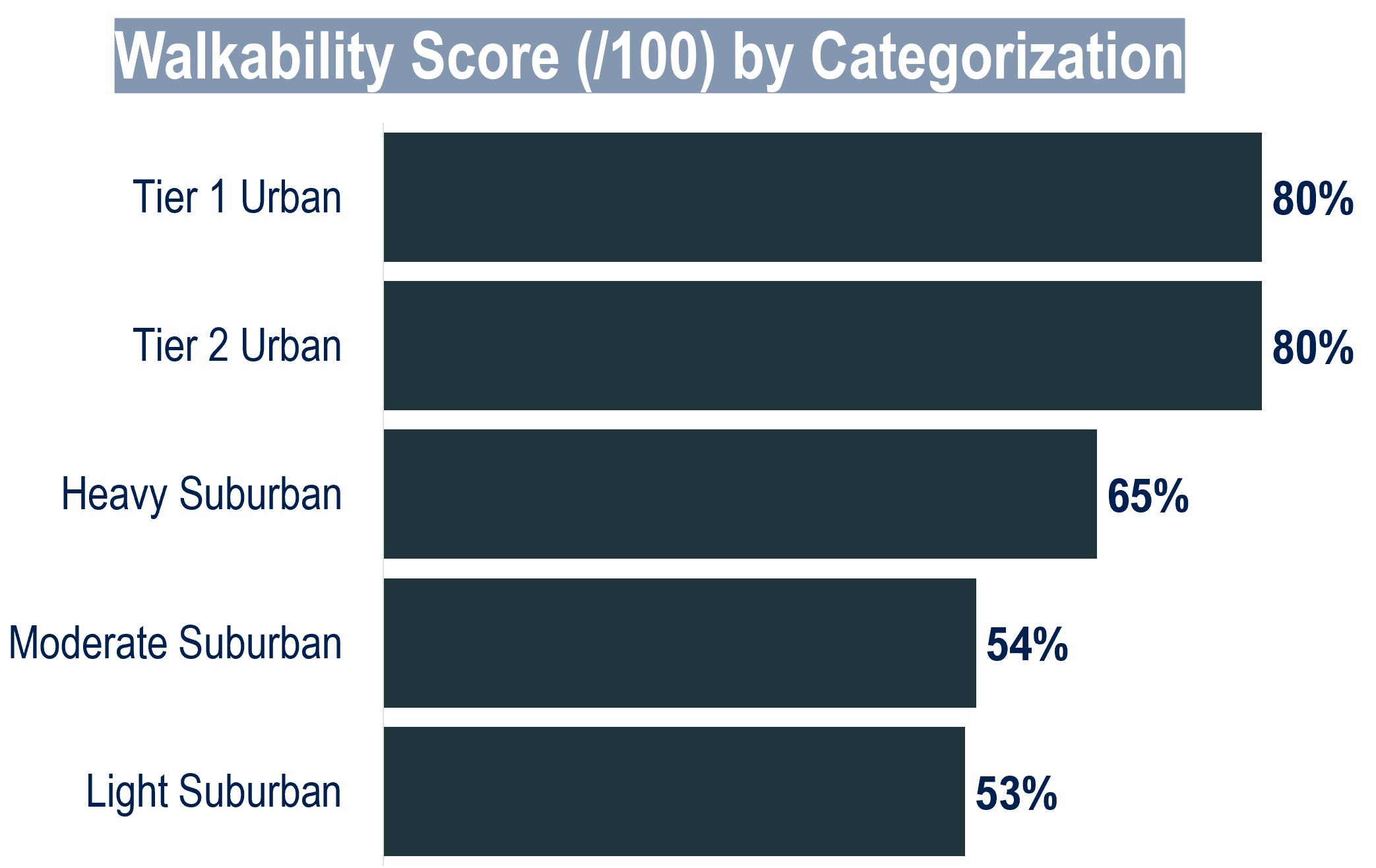
The surrounding area of a typical Apple store is highly accessible either by foot or car.
Urban stores are in highly walkable areas (as measured by a mix of residential & employment density, road network density, and other relevant indicators).
Stores in more suburban areas are less walkable but still accessible. These will typically be in upscale shopping centers or malls where the surrounding area may not be walkable but the location itself is.
Apple is a destination retail location. It drives foot traffic and high-value customers to an area.
Which retailers most commonly locate near an Apple store?
We searched within a 1-mile radius of all Apple stores and included a number of common chains in our search.
We found, by far, the most common brand to be located near an Apple Store is Starbucks, where there is ~96% overlap - 96% of Apple stores have a Starbucks within 1-mile.
The mix of food and beverage and retail stores commonly located near an Apple show that it’s in mixed use environments surrounded by complementary retail experiences for customers.
Consider the location near Naples, FL. The store is located in a high-end outdoor shopping mall called Waterside Shops. Other retailers include Gucci, Tesla, Tiffany & Co, Louis Vuitton…(you get the idea - high end).
The shopping mall is located off a road with 50,000 daily car traffic and is a stone’s throw to the beach.
This location is representative of its strategy - high reach, strong surrounding retail brands, and a wealthy community.
Final Thoughts
Apple is in a unique position to leverage its store footprint to drive cross-channel sales. The sale counts the same whether a customer tries a product in a store then buys online, completes the process fully online, or purchases in-store.
Its omnichannel presence allows it to use stores as showrooms, customer support centers, and retail. As a destination store, they can afford to make the tradeoff of reach over density. They just need to be convenient enough, not on every block.
The analysis above shows they achieve this goal quite well reaching 25% of the US population across their stores within just a 5-mile radius.
Apple’s ability to build great products also extends to its market planning. While not a surprise given its stature and track record of success, it’s nevertheless interesting to dive into the data and see just how strong their location strategy is to reach their target customer across the country.
Interested in this topic? Get in touch with me here or by email at jordan@jordanbean.com.